Insurance plays a critical role in safeguarding individuals, businesses, and assets from unforeseen risks. Among the various types of insurance policies available, first-party and third-party insurance hold significant importance. Understanding the differences between these two types can help policyholders choose the right coverage for their needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into what is first party and third party insurance, their differences, and their applications with step-by-step guidance and real-life examples.
Introduction to First Party and Third Party Insurance
Understanding the different purposes of first party and third party coverage is essential to ensuring that you have the correct type of insurance for your specific needs. Both types offer protection but operate under different mechanisms and serve distinct parties in an insurance contract.
In order to understand the difference between first party and third party insurance, let’s look at the different parties in insurance process.
Parties Involved in Car Insurance
First-Party
The first party is the policyholder or vehicle owner who has opted for coverage from an insurance provider.
Second-Party
The second party is always the insurance provider that the first party purchases the policy from.
Third-Party
The third party is anyone who suffers injury or property damage due to the actions of the first party.
What is First-Party Car Insurance?

First-party insurance is a type of coverage where the insured (policyholder) is protected for their own losses. First-party insurance works on the principle of indemnity, meaning that if the insured (first party) suffers a loss or damage, they can directly claim compensation from the insurance company (second party).
When an insured event occurs (such as an accident, illness, or property damage), the policyholder is compensated by their insurance company.
Example of First Party Insurance
Scenario: Emma has homeowners’ insurance. A severe storm damages the roof of her house. Since her insurance policy includes coverage for storm damage, she filed a first-party claim with her insurer. The company sends an adjuster to assess the damage, and Emma receives compensation to cover the repair costs.
Also read: Difference Between Comprehensive And Zero Depreciation Insurance
Steps To Understand What Is First Party Insurance
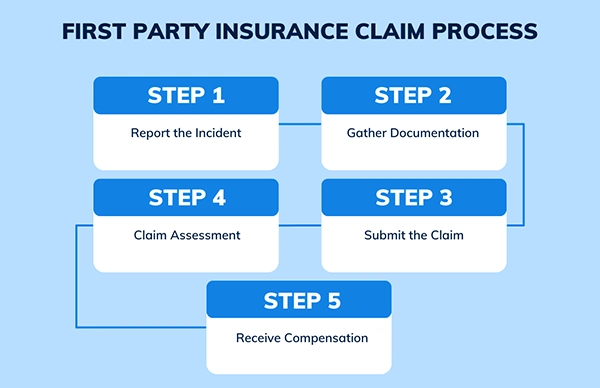
Filing a first-party insurance claim involves several important steps to ensure that the claim is processed smoothly and efficiently.
What is Third Party Car Insurance?
Now, let’s understand what is the meaning of third party insurance. Third-party insurance is a type of liability coverage where the insured (first party) is protected against claims made by another party (third party). In this arrangement, the insured holds the policy, and the third party is someone who is affected by the insured’s actions.
What does third party insurance cover? Third-party insurance provides compensation to the third party for damages caused by the insured.
Example of Third Party Insurance
Scenario: Alex is driving his car when he accidentally hits another vehicle, damaging the bumper. The other driver files a claim against Alex’s third-party insurance. Alex’s insurer reviews the claim, and the other driver receives compensation for the repair.
Steps to Understand What Is Third Party Insurance
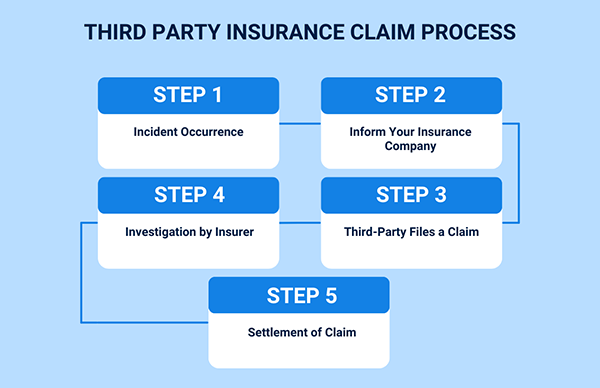
Third-party claims work differently, as the claim is filed by a third party against the insured.
Difference Between First Party Insurance Vs Third Party Insurance
Understanding what is first party and third party insurance and the differences between them is essential for policyholders to make informed decisions. The key distinctions lie in the coverage, relationship, and type of claims made under each policy.
What is first party and third party insurance?
| Aspect | What Is 1st Party Insurance? | What Is 3rd Party Insurance? |
|---|---|---|
| Who is covered? | The first party (the policyholder) | A third party (someone who suffers injury or damage due to the policyholder) |
| Who is not covered? | Does not cover damages caused to a third party | Does not cover damages caused to the insured |
| Coverage Type | Covers various types of losses, such as property damage, personal injuries, and medical expenses. | Covers legal liability for damages or injuries caused to others. |
| Mandatory | Optional for some types of insurance, like comprehensive car insurance. | Legally required in certain cases, such as motor vehicle insurance. |
| Examples | Health insurance, Own Damage (OD) car insurance. | Third-party car insurance, liability insurance for businesses. |
Conclusion

Choosing between first-party and third-party insurance depends on your needs and the type of protection you seek.
First-party insurance is ideal for those who want coverage for their losses, such as damage to property or medical expenses. On the other hand, third-party insurance is essential for protecting against legal liabilities when causing harm or damage to others.
Both types of insurance serve vital purposes, and in some cases, having both can offer better all-round protection. For example, motor vehicle owners often combine first-party (OD) and third-party insurance to cover both their losses and liability toward others.
Leave a comment if this blog helped you understand ‘What is first party and third party insurance?’ Stay updated on motorcycle insurance renewal and IDV in bike insurance by navigating to the Vehicle Information tab.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of third party insurance?
Third party insurance benefits include compensation for third-party injuries and property damage, financial and legal protection, and peace of mind.
What does third party insurance cover?
Third-party insurance covers the legal liabilities of the insured if they cause injury or damage to another person or their property.
First party insurance kya hota hai?
First-party insurance ya pratham-paksh beema ek prakaar ka kavarej hai jahaan yadi beemaadhaarak (pratham paksh) ko nukasaan ya kshati hotee hai, to ve seedhe beema kampanee (dviteey paksh) se muaavaje ka daava kar sakate hain.
What is third party insurance meaning?
In third-party insurance, the insurance firm compensates a third party for any injury or damage that is caused by the first party or policyholder.
Is first-party insurance mandatory in India?
No, only third-party insurance is mandatory in India.















