Petrol engine VS diesel engine– which one is superior? This question has riddled aspiring car owners and car enthusiasts alike.
Both petrol and diesel are made from long chains of hydrocarbons, produced through fractional distillation of crude oil. While petrol is known for its agility and rapid acceleration, diesel reigns supreme in terms of torque and fuel efficiency. Both these automotive power fuels garner varied feedback in terms of performance and driving experience.
Let’s finally settle this ‘feud of the fuels’, by getting an in-depth understanding of the difference between diesel and petrol engines.
What is a Petrol Engine?
Also known as gasoline engine, the petrol engine is an internal combustion engine (ICE) that is made to work on petrol.
Features of Petrol Engine:
- Fuel used: A petrol engine uses petrol to work.
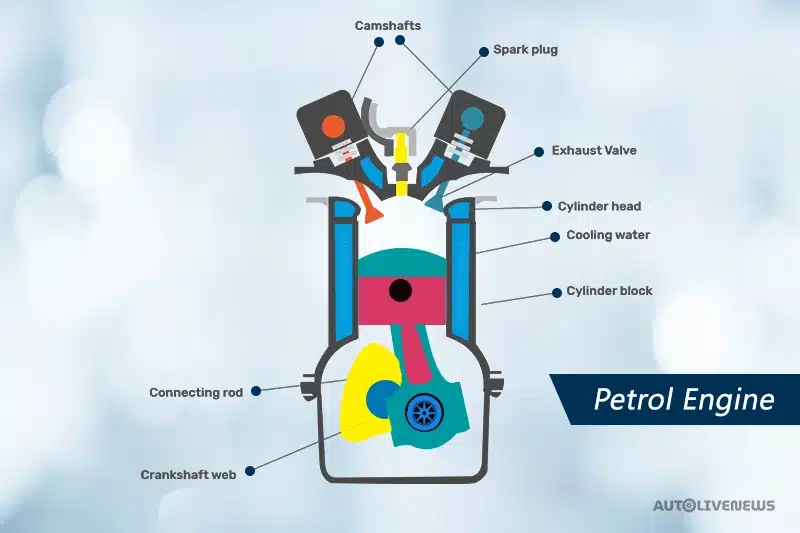
- Internal Combustion Process: The process involves four steps: intake, mixture, power generation, and expel. The engine takes in a mixture of air and petrol inside the cylinder. The piston then mixes them. After that, the spark plug ignites the mixture causing an explosion that pushes the piston down and all the burnt gases are expelled through the exhaust. We’ll discuss the details of the petrol engine working later.
- Ignition: In this type of engine, the spark plug is used to generate ignition in the air-fuel mixture.
- Cooling system: Petrol engines use a water-based cooling system to avoid overheating.
- Lubrication: Motor/engine oil is used in petrol engines to lubricate.
How Does The Petrol Engine Work?
Petrol engines use a process called Internal Combustion, which refers to the process of releasing energy from a fuel and air mixture.
Internal Combustion Engines specifically convert the chemical energy from the fuel to mechanical energy. This energy is what creates the rotary motion in the engine, subsequently setting the car in motion.
In a petrol engine, petrol is first mixed with the air and later on compressed by pistons. Then sparks from spark plugs ignite it.
Let’s get into exactly how the petrol engine works. The fuel (petrol) is mixed with air. This mixture is inducted into the cylinder. After the intake of this mixture, the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture. This ignites a spark leading to combustion. The combustion process leads to the expansion of gases. This expansion pushes the piston during the power stroke.
What is a Diesel Engine?
Similar to the petrol engine, a diesel engine is also an internal combustion engine. However, in this case, air is compressed by the pistons first, and then mixed with the fuel. No spark plug is needed here, as the compressed air ignites the fuel. That is how mechanical energy is produced and the car moves forward.
Features of a Diesel Engine:
- Fuel used: A diesel engine uses diesel to work.
- Internal Combustion Process: The process involves a few steps. Firstly, the air is taken into the cylinders and compressed by the pistons. This is done to generate heat. This heat then mixes with diesel to produce chemical energy. The combustion pushes the piston back and converts chemical energy into mechanical energy.
- Ignition: In this type of engine, compression is used to generate ignition in the air-fuel mixture.
- Cooling system: Diesel engines use a closed-loop, jacket-type cooling system cooling system to avoid overheating.
- Lubrication: Specialized diesel engine oil is used in diesel engines to lubricate.
How Does the Diesel Engine Work?
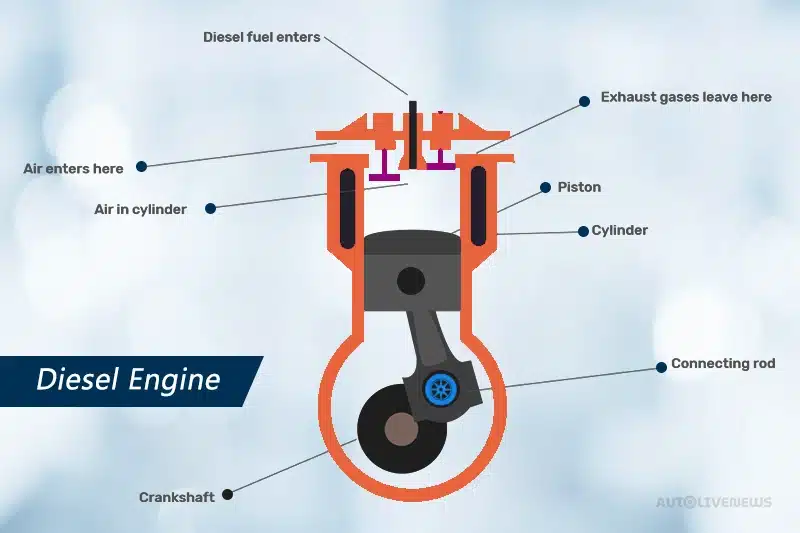
The measure of a diesel engine’s efficiency lies in its ability to convert fuel into mechanical energy. For this it uses the process of internal combustion too, however, it differs a lot from the petrol engine. In diesel engines, the air is taken into the cylinder of the engine. After that, it compressed the piston to increase the temperature in the cylinder. After the temperature rises to a certain extent, fuel (here diesel) is released. After the fuel comes in contact with high temperatures, it creates energy that drives the piston.
Petrol Engine vs Diesel Engine: Let’s Settle the Debate
Although petrol and diesel seem similar in theory, their engines have distinct characteristics, each with unique pros and cons. Now that we know about the two engines and their functioning, let us directly compare petrol and diesel engines, based on important factors that buyers consider while buying a new car:
| No. | Point of Differentiation | Petrol Engine | Diesel Engine |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintenance | Requires less frequent maintenance due to the presence of simpler components. Timing belts may need periodic replacements though. | It requires more maintenance due to complex components. These components require special care due to which maintenance becomes rigorous. |
| 2. | Durability | Less durable than diesel engines making them less reliable. | Lasts longer than a petrol engine as diesel is a lighter fuel. It lubricates the engine well, reducing wear and tear. |
| 3. | Consistency | Consistent performance across various driving conditions even in high RPM ranges. Well suited for high-speed cruising. | Consistent performance but in low RPM ranges. Well suited for towing and hauling. |
| 4 | Driving Experience | They have a smoother and finer driving experience as they produce very low sounds. Modern technology made these cars quieter and more pleasant. | They are known for their noisy driving experience. Even though modern technology has reduced the noise significantly, it is still noisy as compared to petrol engines. |
| 5. | Fuel Efficiency | Low fuel efficiency which makes them not optimal for city driving. | They are highly fuel efficient, especially on highways. |
| 6. | Power | They provide high peak power. | Do not match the power of petrol engines. |
| 7. | Speed | Provide high-speed making them ideal for sports cars. | Have lower speed but better-pulling power at lower RPM. |
| 8. | Energy Efficiency | Are low energy efficient due to high fuel consumption and low thermal efficiency. | Are highly energy efficient due to low fuel consumption and high thermal efficiency. |
| 9. | Ignition Process | They use spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture. | They rely on compression ignition; the high compression ignites the air-fuel mixture. |
| 10. | Longevity | They are not known to last long, especially in harsh conditions. | They are known for their robust longevity. Designed to last longer. |
| 11. | Cost Effective | Initial investments are low. However, with increasing fuel prices, the operational costs are high. | Initial investment here is higher but on the other hand, fuel is cheaper. This reduces the cost significantly. |
| 12. | Temperature | The engine operates at lower temperatures and lacks thermal efficiency. This leads to smooth function of the engine but it causes inefficient combustion. | It operates at a higher level by increasing the temperatures within the engine. This causes efficient combustion but causes stress on the engine reducing the lifespan of the engine. |
| 13. | Environmental Impact | Lower emissions of particulate matter but higher emissions of greenhouse gases. | Lower emissions of greenhouse gases but higher emissions of particulate matter. However, new technology is reducing it. |
| 14. | Engine Design | Simpler design with fewer components making it easy to maintain and repair. | More complex designs with complex components that require specialized maintenance. |
| 15. | Components | They are made up of simpler components. Key components include the engine block, cylinder head, pistons, connecting rods, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors. | They are made up of more complex components like turbochargers, direct fuel injection systems, and particulate filters. |
Fuel Types and Combustion:
Now that we know what is the difference between petrol and diesel engine, let us look into the points of differentiation of the two fuels:
| No. | Point of Differentiation | Petrol | Diesel |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Volatility | Petrol/ gasoline is a lighter and more volatile fuel. | Diesel is a heavier and less volatile fuel. |
| 2. | Ignition | Petrol uses spark plugs to ignite the air-fuel mixture. | Diesel uses compression to ignite the air-fuel mixture. |
| 3. | Fuel- efficiency | Petrol is known to be less fuel efficient. | Diesel is more fuel efficient, especially for high mileage. |
| 4. | Drive | Petrol provides a smoother and quieter drive. | Diesel generally doesn’t provide a smooth drive. |
| 5. | Performance | Provides good speed and power. | Provides lesser speed as compared to petrol. |
| 6. | Cost | The cost of petrol is high and increasing day by day. This is causing a major increase in the operational cost. | Whereas, diesel is a cheaper fuel. Thus, it compensates for its high initial investment. |
Difference Between Diesel and Petrol Engine Oil:
One very important aspect of a diesel engine vs a petrol engine is the difference between the engine oil used. Diesel is the fuel used in a diesel engine, while ‘diesel engine oil’ is used to refer to a lubricating fluid used in an engine to reduce friction. Similarly, petrol is the fuel and ‘petrol engine oil’ is used for lubricating and reducing wear and tear.
| No. | Point of Differentiation | Petrol Engine Oil | Diesel Engine Oil |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Viscosity | This has a lower viscosity as petrol engines work at low temperatures and pressures. | Has a higher viscosity as diesel engines work at high temperatures and pressures. |
| 2. | Additives | Contains additives to prevent oxidation, corrosion, and wear, and to enhance performance. | Contains additives to keep the engine clean and prevent buildup |
| 3. | Detergent and Dispersant Properties | Contains them but they are less potent. | Has stronger detergent and dispersant properties to help with soot buildup. |
Current Market Share and Future Outlook:
For decades, diesel-powered vehicles have been the dominant force on the road. However, in the past few years, the advancement of alternative technology and rising consciousness towards sustainability have introduced the world to the advantages of electric vehicles (EVs). On a global scale, petrol and diesel-engine cars still make up about 50% of car sales. However, the rising popularity of electric commercial vehicles and hybrids is expanding their influence in the market.
Governments and other international bodies have begun implementing stringent emission limits as a measure to tackle the climate crisis. It is predicted that in the next 5 years, the global market share of petrol and diesel vehicles will further drop as EVs will take over around 18% of the share.
Conclusion:
Analysing factors like consistency, durability, fuel efficiency, cost-effectiveness, speed, power and much more elucidates the difference between petrol and diesel engines. It is clear that both of them come with their own advantage and disadvantage. Diesel offers higher longevity and mileage; petrol is known for its greater speed and burns cleaner. This could explain the petrol engine’s higher position in comparison with diesel in terms of usage.
However, please keep in mind every individual has their preferences and expectations from their vehicle, and their choice of fuel should be as per their own priority. But here’s what we suggest if you are trying to settle the dilemma of diesel engine vs petrol engine:
Buy a Diesel Engine if:
- You have a high-mileage use
- Are looking for a more durable option
- Want to reduce your operational cost
Buy a Petrol Engine if:
- You are looking for a cheaper investment
- You want a smoother and faster performance
- Looking for low maintenance car
Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs)
Which car is better, petrol or diesel?
It depends on your priority. If you’re looking for fuel efficiency, longevity, and better insurance premiums, then diesel cars are your go-to. If affordability and environmental sustainability are your lookout, go for petrol cars.
Are diesel engines worth it in 2025?
The rise of eco-friendlier options and a government-imposed ban on old diesel vehicles has slightly dimmed the appeal of diesel engines. However, diesel cars will continue to be relevant in 2025. For those who have to travel large distances and save on fuel, diesel continues to be a coveted option.
Why is petrol not used in diesel engines?
Petrol is never used in diesel engines because it is extremely volatile. This means it could ignite quickly during the compression stroke. This could severely damage the engine.
How to identify petrol or diesel?
Diesel is denser than petrol. Petrol evaporates faster. Check the fuel cap as many vehicles have a label there, suggesting it is petrol/diesel run. Their engine sound differs too. Diesel engines tend to be louder, whereas diesel engines are quieter in operation.
Are diesel engines high maintenance?
Diesel engines have complex components. They often encounter issues with fuel injections, emission systems and turbochargers. Hence, they require frequent and advanced maintenance.
Are diesel cars good for city driving?
No, diesel cars are the preferred choice for long-distance travel. They are not recommended for a low-mileage commute. Petrol cars can be better for intra-city travel.
Which engine life is better, petrol or diesel?
The main petrol and diesel engine difference is that the latter are generally more long-lasting if maintained properly. Heavy-duty vehicles with diesel engines are considered more reliable because of their higher longevity and fuel efficiency.